About DIGIPIN Number
Revolutionizing Location Identification in India
DIGIPIN Number is transforming how we identify and share locations across India through a groundbreaking digital geocoding system.
Developed through a collaborative effort between India Post, IIT Hyderabad, and ISRO, DIGIPIN Number creates a standardized addressing system that converts complex geographic coordinates into simple, easy-to-share 10-character codes.
Why DIGIPIN Number Matters:
- Simplifies navigation to locations without traditional addresses
- Improves emergency response times when every second counts
- Enhances delivery efficiency for postal and courier services
- Supports rural development by providing standardized addressing
- Empowers digital governance with location-based precision
While the traditional PINCODE system (introduced in 1972) serves for larger geographical areas, DIGIPIN Number provides precision down to 3×3 meters - enabling users to share exact locations with unprecedented accuracy.
DIGIPIN Number vs PINCODE
PINCODE
6-digit code covering large postal delivery areas
DIGIPIN Number
10-character alphanumeric code providing precision to 3 meters
The Evolution of Digital Addressing in India
PINCODE Introduced
6-digit codes for postal sorting areas
Research Begins
Collaboration with IIT Hyderabad and ISRO
Beta Release
Initial testing and public feedback
National Implementation
Expanding across India
How DIGIPIN Number Works?
DIGIPIN: Code Architecture
The Detailed structure is such that the DIGIPIN is essentially an encoding of the latitude and longitude of the address into a sequence of alphanumeric symbols using the following 16 symbols: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, C, J, K, L, M, P, F, T.
The process of identifying the cells is done in a hierarchical fashion. The encoding is performed at various levels, and the basic idea is the following:
- A bounding box is used that covers the entire country.
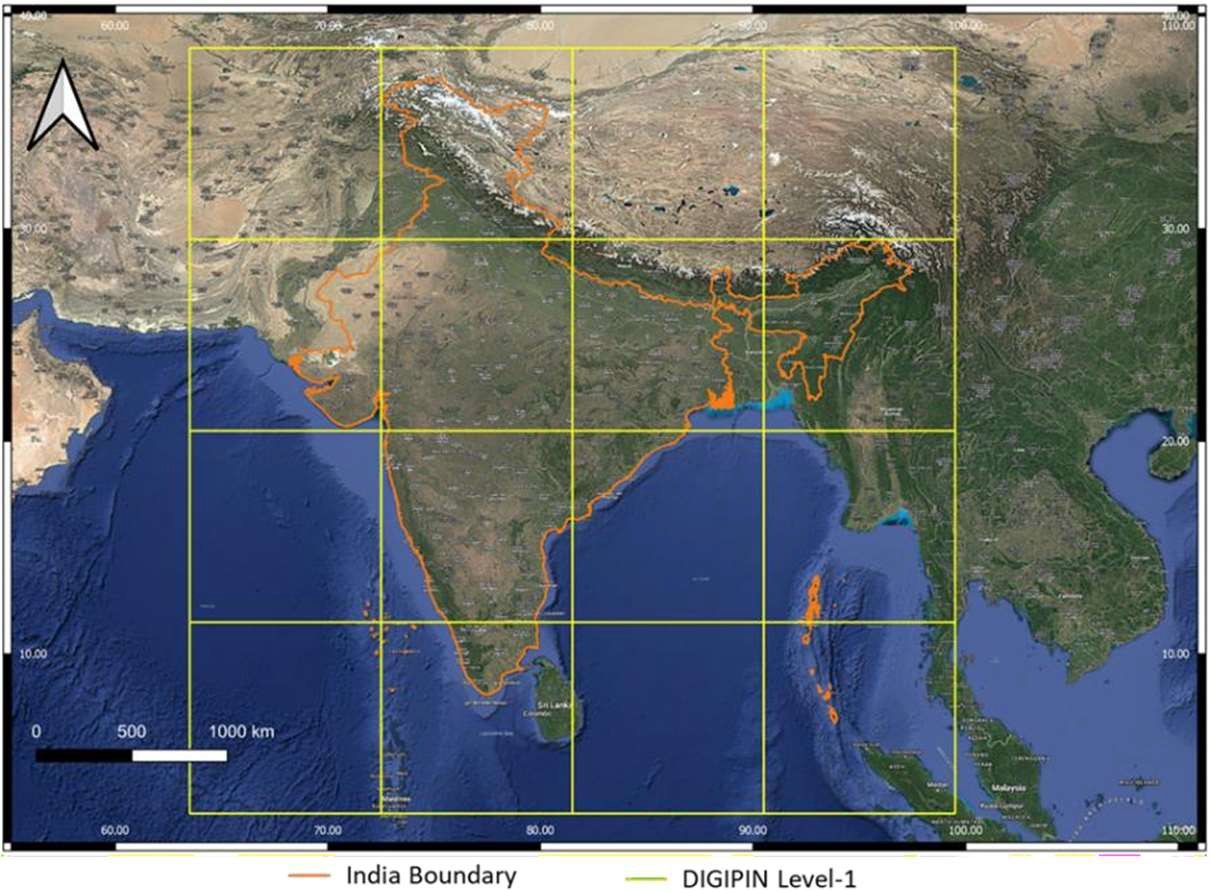
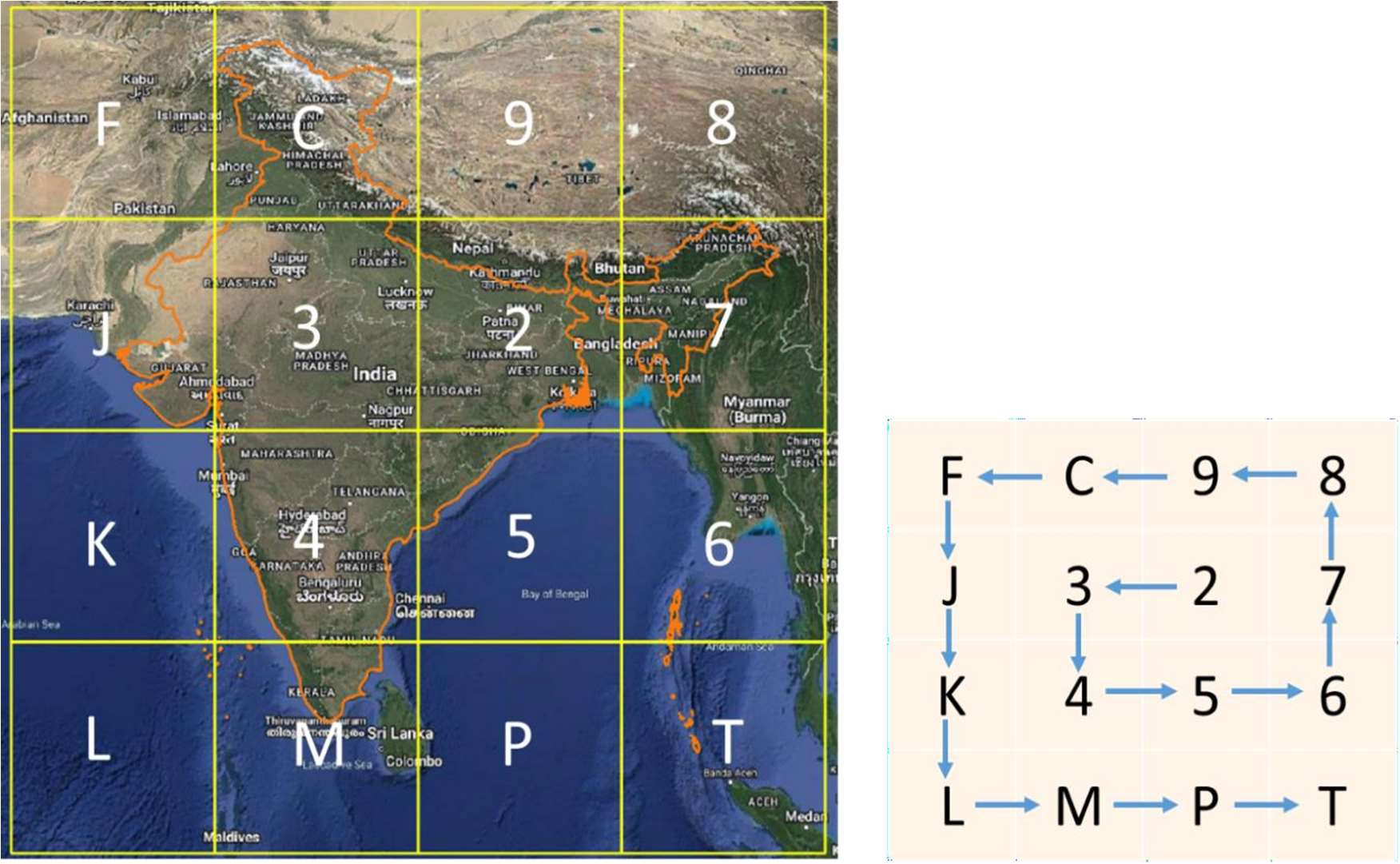
- The bounding box is split into 16 (i.e., 4x4) regions. Each region is labeled by one of symbols 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, C, J, K, L, M, P, F, T. The first character in the code would identify one of these regions. This is called the level-1 partition.
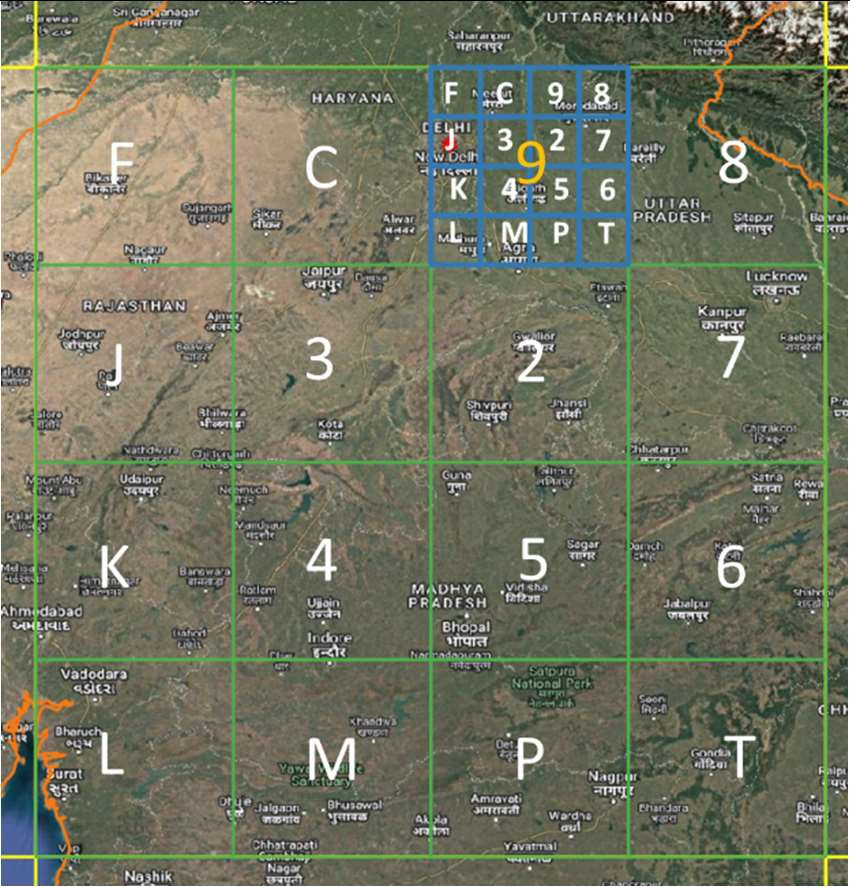
- Each region is then subdivided into 16 subregions in a similar fashion. Each of the 16 subregions are labeled by the 16 characters. For a given region, the subregion is identified by the second character of the code. Therefore, the first two characters of the code uniquely identify one of the 16^2=256 subregions. This is called the level-2 partition.
- The encoding of successive characters, and therefore the next 8 levels is done in an identical fashion. The 10-symbol code therefore uniquely identifies one of the 16x10 cells within the bounding box.
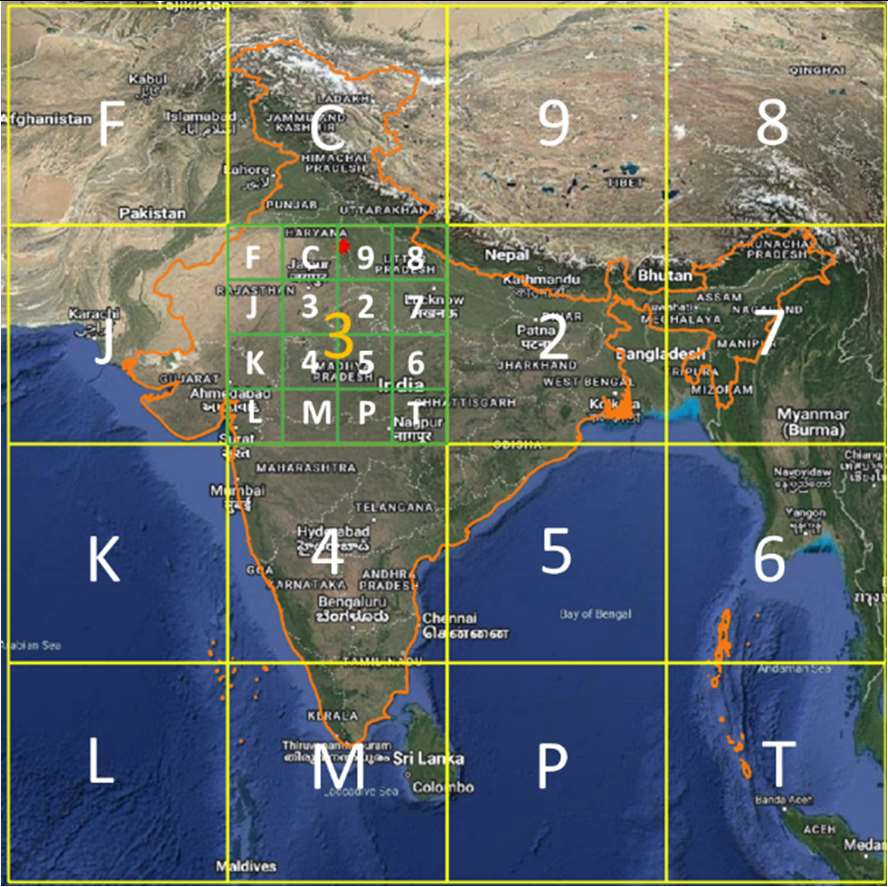
Bounding Box:
Following are the details of the bounding box used:
- Longitude 63.5 – 99.5 degrees east
- Latitude 2.5 – 38.5 degrees north
- The Coordinate Reference System (CRS) used in the proposed code design is EPSG:4326. Using EPSG:4326 (also known as WGS84) has several advantages like wide recognition and adoption, simplicity and global coverage
The choice of the corner points of the bounding box are based on the following considerations:
- This includes the entire territory of India.
- Includes the maritime Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), and therefore DIGIPIN allows to provide addresses to Indian assets in the sea (oil rigs, future man-made islands, etc.).
- The Indian mainland is covered by only 8 regions, and therefore can be labeled with the digits 2-9 at level-1.
Labelling of Regions at Various Levels
Level 1:
- Level-1 labelling ensures that the mainland is labelled using only the digits 2-9.
- Codewords starting with P, W and X are reserved for future or special uses
Level 2:
- Each Level-1 region is further split into 16 sub-regions called Level-2 regions as illustrated in the figure. The regions are hierarchically partitioned into sub-regions in an identical fashion.
DIGIPIN Levels and Precision
| DIGIPIN Level | Example Code | Area Covered | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (1 character) | 7 | Large region (~200 x 200 km) | Identifying major regions |
| Level 2 (2 characters) | 7P | ~50 x 50 km | District level identification |
| Level 5 (5 characters) | 7P-3K | ~1 x 1 km | Village or town area identification |
| Level 10 (10 characters) | 7P-3K-J5CP | ~3 x 3 meters | Precise location identification |
Level 2 Grid
Division into 16 sub-regions from level 1
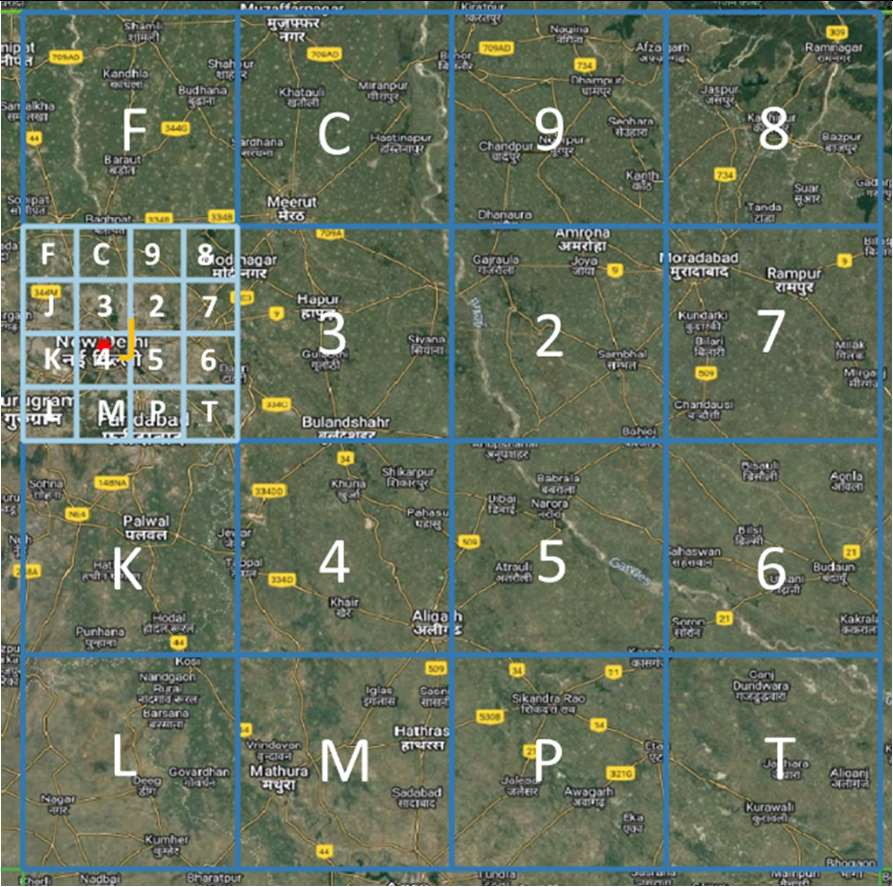
Level 3 Grid
Increased precision with 3-character codes
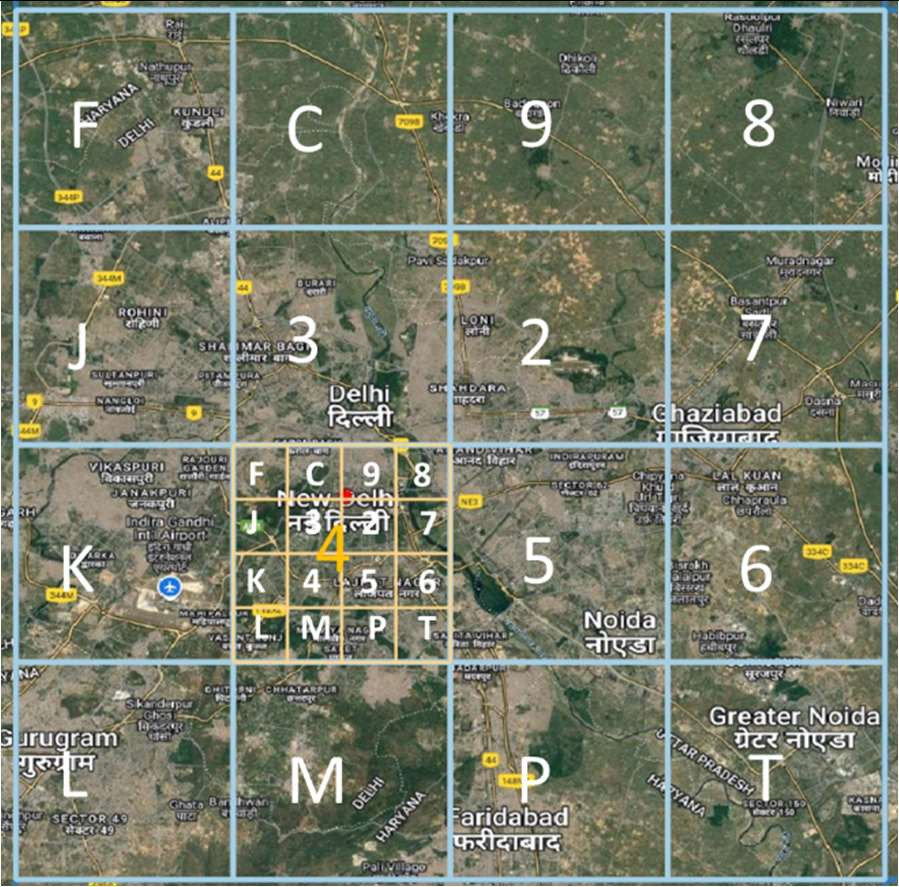
Level 4 Grid
Narrowing down to smaller areas
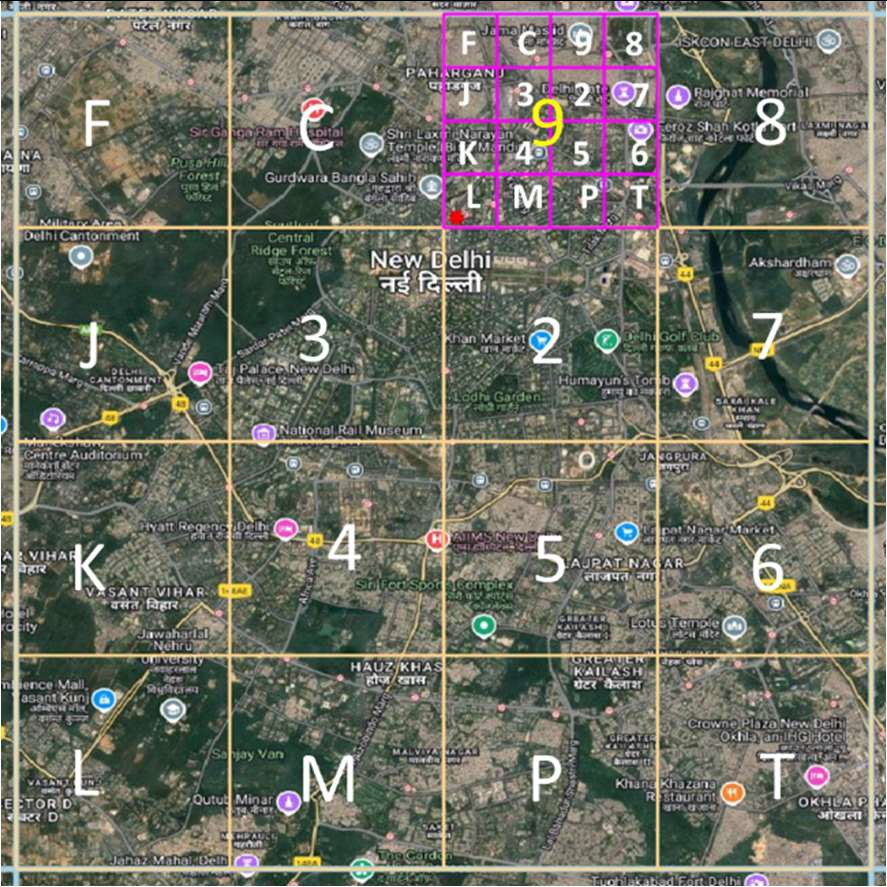
Level 5 Grid
Village/town level precision
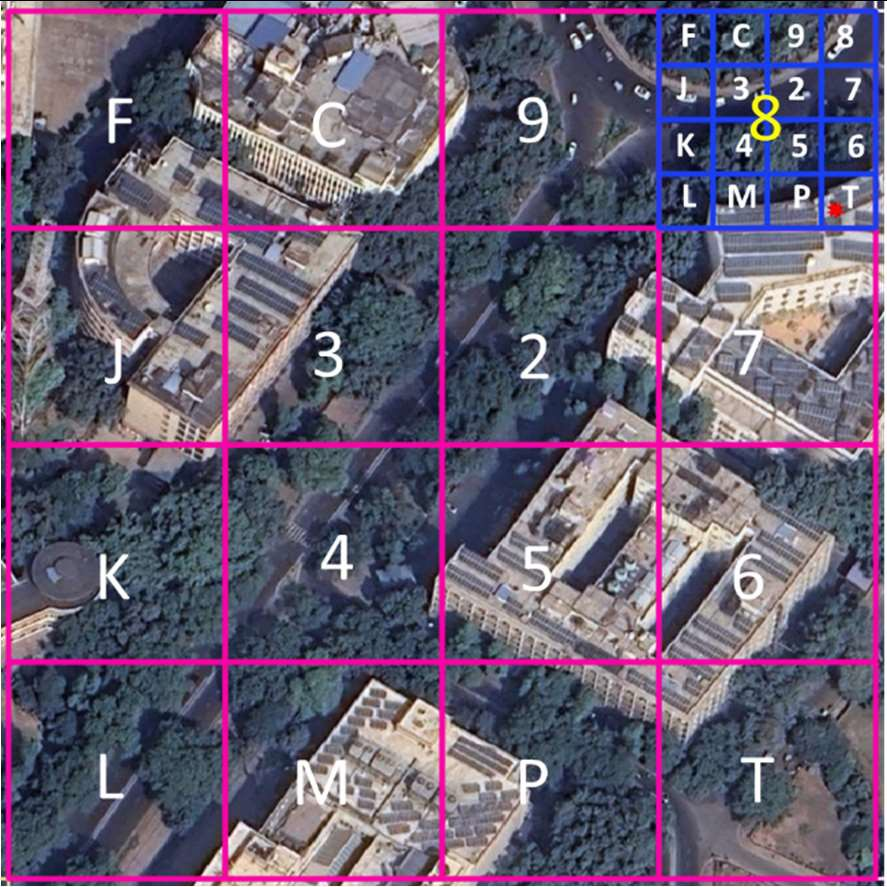
Level 8 Grid
Street-level precision for accurate navigation

Level 10 Grid
Precise location identification (3×3 meters)